Class 10 Maths Solutions Chapter 1 Arithmetic Progressions Exercise 1.3
Question 1
Find the sum of the following APs.
(i) 2, 7, 12 ,…., to 10 terms.
(ii) − 37, − 33, − 29 ,…, to 12 terms
(iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8 ,…….., to 100 terms
(iv) 1/15, 1/12, 1/10, …… , to 11 terms
Answer:
(i) 2, 7, 12, …, to 10 terms.
For this A.P
a = 2
d = a₂ − a₁ = 7 − 2 = 5
n = 10
We know the formula for the sum of the first n terms is:
Sn = n / 2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values:
S₁₀ = 10 / 2 [2(2) + (10 – 1) × 5]
S₁₀ = 5 [4 + (9) × 5]
S₁₀ = 5 × 49 = 245
Therefore, the sum of the first 10 terms is 245.
(ii) −37, −33, −29, …, to 12 terms.
For this A.P.:
a = −37
d = a₂ − a₁ = −33 − (−37) = 4
n = 12
We know the formula for the sum of the first n terms is:
Sn = n / 2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values:
S₁₂ = 12 / 2 [2(−37) + (12 – 1) × 4]
S₁₂ = 6 [−74 + (11) × 4]
S₁₂ = 6 × [−74 + 44]
S₁₂ = 6 × (−30) = −180
Therefore, the sum of the first 12 terms is −180.
(iii) 0.6, 1.7, 2.8, …, to 100 terms.
For this A.P.:
a = 0.6
d = a₂ − a₁ = 1.7 − 0.6 = 1.1
n = 100
We know the formula for the sum of the first n terms is:
Sn = n / 2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values:
S₁₀₀ = 100 / 2 [2(0.6) + (100 – 1) × 1.1]
S₁₀₀ = 50 [1.2 + (99) × 1.1]
S₁₀₀ = 50 × [1.2 + 108.9]
S₁₀₀ = 50 × 110.1 = 5505
Therefore, the sum of the first 100 terms is 5505.
(iv) 1/15, 1/12, 1/10, …, to 11 terms.
For this A.P.:
a = 1/15
d = a₂ − a₁ = 1/12 − 1/15 = (5 – 4) / 60 = 1/60
n = 11
We know the formula for the sum of the first n terms is:
Sn = n / 2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values:
S₁₁ = 11 / 2 [2(1/15) + (11 – 1) × 1/60]
S₁₁ = 5.5 [2/15 + (10) × 1/60]
S₁₁ = 5.5 [2/15 + 10/60]
S₁₁ = 5.5 [8/60 + 10/60]
S₁₁ = 5.5 × 18/60
S₁₁ = 5.5 × 3/10 = 1.65
Therefore, the sum of the first 11 terms is 1.65.
So, the answers are:
(i) 245
(ii) −180
(iii) 5505
(iv) 1.65
Question 2
Find the sums given below
(i) 7 + 10(1/2)+ 14 + ……………… +84
(ii)+ 14 + ………… + 84
(ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + ……….. + 10
(iii) − 5 + (− 8) + (− 11) + ………… + (− 230)
Answer:
(i) 7 + 10.5 + 14 + … + 84
For this A.P.:
a = 7
d = 10.5 – 7 = 3.5
The last term is 84.
We use the formula for the nth term of an A.P.: an = a + (n – 1) d
Substitute the values: 84 = 7 + (n – 1) × 3.5 84 – 7 = (n – 1) × 3.5 77 = (n – 1) × 3.5 n – 1 = 77 ÷ 3.5 n – 1 = 22 n = 23
Now, we use the sum formula: Sn = n / 2 × [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values: S23 = 23 / 2 × [2(7) + (23 – 1) × 3.5] S23 = 23 / 2 × [14 + 77] S23 = 23 / 2 × 91 S23 = 23 × 45.5 S23 = 1046.5
Therefore, the sum is 1046.5.
(ii) 34 + 32 + 30 + … + 10
For this A.P.:
a = 34
d = 32 – 34 = -2
The last term is 10.
We use the formula for the nth term of an A.P.: an = a + (n – 1) d
Substitute the values: 10 = 34 + (n – 1) × (-2) 10 – 34 = (n – 1) × (-2) -24 = (n – 1) × (-2) n – 1 = -24 ÷ -2 n – 1 = 12 n = 13
Now, we use the sum formula: Sn = n / 2 × [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values: S13 = 13 / 2 × [2(34) + (13 – 1) × (-2)] S13 = 13 / 2 × [68 + 12(-2)] S13 = 13 / 2 × [68 – 24] S13 = 13 / 2 × 44 S13 = 13 × 22 S13 = 286
Therefore, the sum is 286.
(iii) −5 + (−8) + (−11) + … + (−230)
For this A.P.:
a = -5
d = -8 – (-5) = -3
The last term is -230.
We use the formula for the nth term of an A.P.: an = a + (n – 1) d
Substitute the values: -230 = -5 + (n – 1) × (-3) -230 + 5 = (n – 1) × (-3) -225 = (n – 1) × (-3) n – 1 = -225 ÷ -3 n – 1 = 75 n = 76
Now, we use the sum formula: Sn = n / 2 × [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values: S76 = 76 / 2 × [2(-5) + (76 – 1) × (-3)] S76 = 38 × [-10 + 75 × (-3)] S76 = 38 × [-10 – 225] S76 = 38 × (-235) S76 = -8930
Therefore, the sum is -8930.
So, the sums are:
(i) 1046.5
(ii) 286
(iii) -8930
Question 3
In an AP
(i) Given a = 5, d = 3, an = 50, find n and Sn.
(ii) Given a = 7, a13 = 35, find d and S13.
(iii) Given a12 = 37, d = 3, find a and S12.
(iv) Given a3 = 15, S10 = 125, find d and a10.
(v) Given d = 5, S9 = 75, find a and a9.
(vi) Given a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90, find n and an.
(vii) Given a = 8, an = 62, Sn = 210, find n and d.
(viii) Given an = 4, d = 2, Sn = − 14, find n and a.
(ix) Given a = 3, n = 8, S = 192, find d.
(x) Given l = 28, S = 144 and there are total 9 terms. Find a.
Answer:
(i) Given a = 5, d = 3, an = 50, find n and Sn.
To find n: Use the formula for the nth term:
an = a + (n – 1) * d
50 = 5 + (n – 1) * 3
45 = (n – 1) * 3
n – 1 = 15
n = 16
Now to find Sn:
Sn = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
Sn = 16/2 * [2(5) + (16 – 1) * 3]
Sn = 8 * [10 + 45]
Sn = 8 * 55
Sn = 440
Answer: n = 16, Sn = 440
(ii) Given a = 7, a₁₃ = 35, find d and S₁₃.
To find d: Use the formula for the nth term:
aₙ = a + (n – 1) * d
35 = 7 + (13 – 1) * d
35 = 7 + 12d
28 = 12d
d = 28 / 12
d = 7 / 3
Now to find S₁₃:
Sₙ = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
S₁₃ = 13/2 * [2(7) + (13 – 1) * (7/3)]
S₁₃ = 13/2 * [14 + (12 * 7 / 3)]
S₁₃ = 13/2 * [14 + 28]
S₁₃ = 13/2 * 42
S₁₃ = 13 * 21
S₁₃ = 273
Answer: d = 7/3, S₁₃ = 273
(iii) Given a₁₂ = 37, d = 3, find a and S₁₂.
To find a: Use the formula for the nth term:
aₙ = a + (n – 1) * d
37 = a + (12 – 1) * 3
37 = a + 33
a = 37 – 33
a = 4
Now to find S₁₂:
Sₙ = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
S₁₂ = 12/2 * [2(4) + (12 – 1) * 3]
S₁₂ = 6 * [8 + 33]
S₁₂ = 6 * 41
S₁₂ = 246
Answer: a = 4, S₁₂ = 246
(iv) Given a₃ = 15, S₁₀ = 125, find d and a₁₀.
To find d: Use the formula for the nth term:
aₙ = a + (n – 1) * d
15 = a + (3 – 1) * d
15 = a + 2d
a = 15 – 2d
Now use the sum formula for S₁₀:
Sₙ = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
125 = 10/2 * [2a + (10 – 1) * d]
125 = 5 * [2a + 9d]
25 = 2a + 9d
Substitute a = 15 – 2d:
25 = 2(15 – 2d) + 9d
25 = 30 – 4d + 9d
25 = 30 + 5d
5d = -5
d = -1
Now find a₁₀:
a₁₀ = a + (10 – 1) * d
a₁₀ = 15 – 2(-1) + 9(-1)
a₁₀ = 15 + 2 – 9
a₁₀ = 8
Answer: d = -1, a₁₀ = 8
(v) Given d = 5, S₉ = 75, find a and a₉.
To find a: Use the sum formula for S₉:
Sₙ = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
75 = 9/2 * [2a + (9 – 1) * 5]
75 = 9/2 * [2a + 40]
150 = 9(2a + 40)
150 = 18a + 360
18a = -210
a = -210 / 18
a = -35/3
Now find a₉:
a₉ = a + (9 – 1) * d
a₉ = -35/3 + 8 * 5
a₉ = -35/3 + 40
a₉ = 85/3
Answer: a = -35/3, a₉ = 85/3
(vi) Given a = 2, d = 8, Sn = 90, find n and aₙ.
To find n: Use the sum formula:
Sₙ = n/2 * [2a + (n – 1) * d]
90 = n/2 * [2(2) + (n – 1) * 8]
90 = n/2 * [4 + 8n – 8]
90 = n/2 * (8n – 4)
180 = n(8n – 4)
180 = 8n² – 4n
8n² – 4n – 180 = 0
2n² – n – 45 = 0
Using the quadratic formula:
n = (1 ± √(1 + 4(2)(45))) / (2 * 2)
n = (1 ± √361) / 4
n = (1 ± 19) / 4
n = 5 or n = -9 (negative value discarded)
Now find aₙ:
aₙ = a + (n – 1) * d
aₙ = 2 + (5 – 1) * 8
aₙ = 2 + 32
aₙ = 34
Answer: n = 5, aₙ = 34
Question 4
How many terms of the AP. 9, 17, 25 … must be taken to give a sum of 636?
Answer:
To find how many terms of the AP 9, 17, 25,… must be taken to give a sum of 636:
First term (a) = 9
Common difference (d) = 8
Sum (Sₙ) = 636
Use the sum formula for an AP:
Sₙ = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Substitute the values:
636 = n/2 [2(9) + (n – 1)8)]
Simplify the equation:
636 = n/2 [8n + 10]
Multiply both sides by 2:
1272 = n(8n + 10)
Rearrange the equation into a quadratic form:
8n² + 10n – 1272 = 0
Solve the quadratic equation:
n = [-10 ± √(10² – 4(8)(-1272))] / 2(8)
n = 11.97 (round up)
Answer: 12 terms
Question 5
The first term of an AP is 5, the last term is 45 and the sum is 400. Find the number of terms and the common difference.
Answer:
First term (a) = 5
Last term (l) = 45
Sum (S_n) = 400
Using the sum formula:
S_n = (n/2) * (a + l)
400 = (n/2) * 50
n = 16
Now, using the nth term formula:
l = a + (n – 1) * d
45 = 5 + 15d
40 = 15d
d = 8/3
Thus, the number of terms is 16, and the common difference is 8/3.
Question 6
The first and the last term of an AP are 17 and 350 respectively. If the common difference is 9, how many terms are there and what is their sum?
Answer:
Given:
a = 17
l = 350
d = 9
Let there be n terms in the A.P.
l = a + (n − 1) d
350 = 17 + (n − 1) * 9
333 = (n − 1) * 9
(n − 1) = 37
n = 38
Sn = n/2 (a + l)
S38 = 38/2 * (17 + 350)
S38 = 19 * 367
S38 = 6983
Thus, this A.P. contains 38 terms and the sum of the terms of this A.P. is 6983.
Question 7
Find the sum of first 22 terms of an AP in which d = 7 and 22nd term is 149.
Answer:
Given:
d = 7
a22 = 149
S22 = ?
Step 1: Find the first term (a)
Using the formula for the nth term of an A.P.:
an = a + (n − 1) d
a22 = a + (22 − 1) * 7
149 = a + 21 * 7
149 = a + 147
a = 149 – 147
a = 2
Step 2: Find the sum of the first 22 terms (S22)
Using the formula for the sum of the first n terms:
Sn = n/2 (a + an)
S22 = 22/2 * (2 + 149)
S22 = 11 * 151
S22 = 1661
Thus, the sum of the first 22 terms is 1661.
Question 8
Find the sum of first 51 terms of an AP whose second and third terms are 14 and 18 respectively.
Answer:
Given that:
a2 = 14
a3 = 18
Step 1: Find the common difference (d)
d = a3 − a2
d = 18 − 14 = 4
Step 2: Find the first term (a)
a2 = a + d
14 = a + 4
a = 10
Step 3: Find the sum of the first 51 terms (S51)
Using the sum formula:
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
S51 = 51/2 [2 × 10 + (51 – 1) × 4]
S51 = 51/2 [20 + 200]
S51 = 51 × 220 / 2
S51 = 51 × 110
S51 = 5610
Thus, the sum of the first 51 terms is 5610.
Question 9
If the sum of first 7 terms of an AP is 49 and that of 17 terms is 289, find the sum of first n terms.
Answer:
Sum of first 7 terms (S7) = 49
Sum of first 17 terms (S17) = 289
Step 1: Use the sum formula of an AP
The sum of the first n terms of an arithmetic progression is given by the formula:
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
For S7 = 49:
S7 = 7/2 [2a + (7 – 1) d]
49 = 7/2 [2a + 6d]
98 = 7 [2a + 6d]
14 = 2a + 6d (Equation 1)
For S17 = 289:
S17 = 17/2 [2a + (17 – 1) d]
289 = 17/2 [2a + 16d]
578 = 17 [2a + 16d]
34 = 2a + 16d (Equation 2)
Step 2: Solve the system of equations
From Equation 1:
2a + 6d = 14
From Equation 2:
2a + 16d = 34
Subtract Equation 1 from Equation 2:
(2a + 16d) – (2a + 6d) = 34 – 14
10d = 20
d = 2
Step 3: Find the first term (a)
Substitute d = 2 into Equation 1:
2a + 6(2) = 14
2a + 12 = 14
2a = 2
a = 1
Step 4: Find the sum of the first n terms (Sn)
Now that we know a = 1 and d = 2, we can use the sum formula:
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1) d]
Sn = n/2 [2(1) + (n – 1) 2]
Sn = n/2 [2 + 2n – 2]
Sn = n/2 * 2n
Sn = n^2
Final Answer:
The sum of the first n terms is n².
Question 10
how that a1, a2 … , an , … form an AP where an is defined as below
(i) an = 3 + 4n
(ii) an = 9 − 5n
Also find the sum of the first 15 terms in each case.
Answer:
For 1) an = 3 + 4n
Step 1: Verify if it forms an AP
a1 = 3 + 4(1) = 7
a2 = 3 + 4(2) = 11
a3 = 3 + 4(3) = 15
The common difference is:
a2 – a1 = 11 – 7 = 4
a3 – a2 = 15 – 11 = 4
Since the common difference is constant (4), it forms an arithmetic progression with first term a = 7 and common difference d = 4.
Step 2: Find the sum of the first 15 terms
The sum of the first n terms is given by the formula:
Sn = n/2 * (2a + (n – 1) * d)
Substitute a = 7, d = 4, and n = 15:
S15 = 15/2 * (2 * 7 + (15 – 1) * 4)
S15 = 15/2 * (14 + 56)
S15 = 15/2 * 70
S15 = 15 * 35 = 525
Thus, the sum of the first 15 terms is 525.
For 2) an = 9 – 5n
Step 1: Verify if it forms an AP
a1 = 9 – 5(1) = 4
a2 = 9 – 5(2) = -1
a3 = 9 – 5(3) = -6
The common difference is:
a2 – a1 = -1 – 4 = -5
a3 – a2 = -6 – (-1) = -5
Since the common difference is constant (-5), it forms an arithmetic progression with first term a = 4 and common difference d = -5.
Step 2: Find the sum of the first 15 terms
Sn = n/2 * (2a + (n – 1) * d)
Substitute a = 4, d = -5, and n = 15:
S15 = 15/2 * (2 * 4 + (15 – 1) * (-5))
S15 = 15/2 * (8 + 14 * (-5))
S15 = 15/2 * (8 – 70)
S15 = 15/2 * (-62)
S15 = 15 * (-31)
S15 = -465
Thus, the sum of the first 15 terms is -465.
Question 11
If the sum of the first n terms of an AP is 4n − n2, what is the first term (that is S1)? What is the sum of first two terms? What is the second term? Similarly find the 3rd, the10th and the nth terms.
Answer:
Given:
Sn = 4n – n²
First term (S1):
S1 = 4(1) – 1² = 3
So, the first term a1 = 3.
Sum of the first two terms (S2):
S2 = 4(2) – 2² = 4
S2 = a1 + a2
4 = 3 + a2
So, a2 = 1.
Second term (a2):
a2 = 1.
Third term (a3):
S3 = 4(3) – 3² = 3
S3 = a1 + a2 + a3
3 = 3 + 1 + a3
So, a3 = -1.
10th term (a10):
S10 = 4(10) – 10² = -60
S9 = 4(9) – 9² = -45
S10 = S9 + a10
-60 = -45 + a10
So, a10 = -15.
Nth term (an):
an = Sn – S(n-1)
an = 4n – n² – (4(n-1) – (n-1)²)
Simplifying gives:
an = -2n + 5
Summary:
First term a1 = 3
Sum of the first two terms is 4
Second term a2 = 1
Third term a3 = -1
10th term a10 = -15
Nth term an = -2n + 5
Question 12
Find the sum of first 40 positive integers divisible by 6.
Answer:
The positive integers that are divisible by 6 are
6, 12, 18, 24 …
It can be observed that these are making an A.P. whose first term is 6 and common difference is 6.
a = 6
d = 6
S40 = ?
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
S40 = 40/2 [2(6) + (40 – 1) 6]
= 20[12 + (39) (6)]
= 20(12 + 234)
= 20 × 246
= 4920
Question 13
Find the sum of first 15 multiples of 8.
Answer:
The multiples of 8 are
8, 16, 24, 32…
These are in an A.P., having first term as 8 and common difference as 8.
Therefore, a = 8
d = 8
S15 = ?
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
S15 = 15/2 [2(8) + (15 – 1)8]
= 15/2[6 + (14) (8)]
= 15/2[16 + 112]
= 15(128)/2
= 15 × 64
= 960
Question 14
Find the sum of the odd numbers between 0 and 50.
Answer:
The odd numbers between 0 and 50 are
1, 3, 5, 7, 9 … 49
Therefore, it can be observed that these odd numbers are in an A.P.
a = 1
d = 2
l = 49
l = a + (n − 1) d
49 = 1 + (n − 1)2
48 = 2(n − 1)
n − 1 = 24
n = 25
Sn = n/2 (a + l)
S25 = 25/2 (1 + 49)
= 25(50)/2
=(25)(25)
= 625
Question 15
A contract on construction job specifies a penalty for delay of completion beyond a certain dateas follows: Rs. 200 for the first day, Rs. 250 for the second day, Rs. 300 for the third day, etc., the penalty for each succeeding day being Rs. 50 more than for the preceding day. How much money the contractor has to pay as penalty, if he has delayed the work by 30 days.
Answer:
It can be observed that these penalties are in an A.P. having first term as 200 and common difference as 50.
a = 200
d = 50
Penalty that has to be paid if he has delayed the work by 30 days = S30
= 30/2 [2(200) + (30 – 1) 50]
= 15 [400 + 1450]
= 15 (1850)
= 27750
Therefore, the contractor has to pay Rs 27750 as penalty.
Question 16
A sum of Rs 700 is to be used to give seven cash prizes to students of a school for their overall academic performance. If each prize is Rs 20 less than its preceding prize, find the value of each of the prizes.
Answer:
Let the cost of 1st prize be P.
Cost of 2nd prize = P − 20
And cost of 3rd prize = P − 40
It can be observed that the cost of these prizes are in an A.P. having common difference as −20 and first term as P.
a = P
d = −20
Given that, S7 = 700
7/2 [2a + (7 – 1)d] = 700
a + 3(−20) = 100
a − 60 = 100
a = 160
Therefore, the value of each of the prizes was Rs 160, Rs 140, Rs 120, Rs 100, Rs 80, Rs 60, and Rs 40.
Question 17
In a school, students thought of planting trees in and around the school to reduce air pollution. It was decided that the number of trees, that each section of each class will plant, will be the same as the class, in which they are studying, e.g., a section of class I will plant 1 tree, a section of class II will plant 2 trees and so on till class XII. There are three sections of each class. How many trees will be planted by the students?
Answer:
It can be observed that the number of trees planted by the students is in an AP.
1, 2, 3, 4, 5………………..12
First term, a = 1
Common difference, d = 2 − 1 = 1
Sn = n/2 [2a + (n – 1)d]
S12 = 12/2 [2(1) + (12 – 1)(1)]
= 6 (2 + 11)
= 6 (13)
= 78
Therefore, number of trees planted by 1 section of the classes = 78
Number of trees planted by 3 sections of the classes = 3 × 78 = 234
Therefore, 234 trees will be planted by the students.
Question 18
A spiral is made up of successive semicircles, with centres alternately at A and B, starting with centre at A of radii 0.5, 1.0 cm, 1.5 cm, 2.0 cm, ……… as shown in figure. What is the total length of such a spiral made up of thirteen consecutive semicircles? (Take π = 22/7)
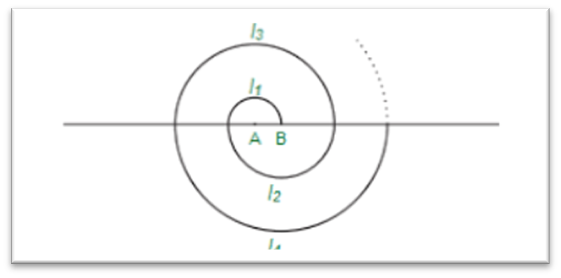
Answer:
Formula for the length of a semicircle:
The length of a semicircle is given by:
Length = π × radius (r).
Radii of the semicircles:
The radii are: 0.5 cm, 1.0 cm, 1.5 cm, 2.0 cm, …, up to 6.5 cm for the 13th semicircle.
Sum of the radii:
The radii follow a pattern: they increase by 0.5 cm each time.
The sum of the first 13 radii is:
Sum = 13/2 × (first radius + last radius)
Sum = 13/2 × (0.5 + 6.5)
Sum = 13/2 × 7 = 45.5 cm.
Total length of the spiral:
Now, multiply the sum of the radii by π (which is 22/7):
Total length = (22/7) × 45.5 = 143 cm.
Question 19
200 logs are stacked in the following manner: 20 logs in the bottom row, 19 in the next row, 18 in the row next to it and so on. In how many rows are the 200 logs placed and how many logs are in the top row?
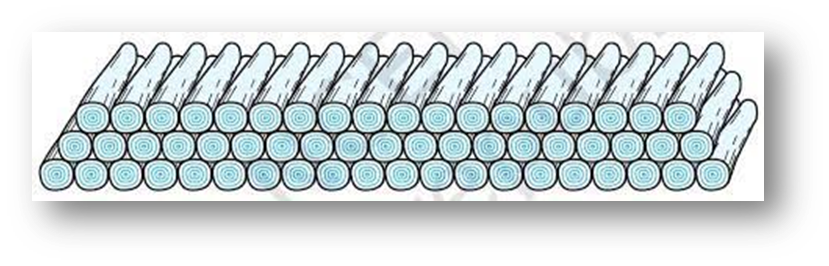
Answer:
We need to find how many rows are there and how many logs are in the top row.
Formula for the sum of logs in the rows:
The sum of the first n rows of logs is given by the formula:
Sn = n/2 × (2a + (n-1) × d)
where:
a = 20 (logs in the bottom row),
d = -1 (common difference),
Sn = 200 (total logs).
Substituting the values:
Substituting into the formula gives:
200 = n/2 × (2 × 20 + (n-1) × (-1))
Simplifying the equation:
200 = n/2 × (40 – n + 1)
200 = n/2 × (41 – n)
400 = n × (41 – n)
400 = 41n – n^2
Solving this quadratic equation gives n = 16.
Logs in the top row:
The number of logs in the top row is:
20 – (16 – 1) = 20 – 15 = 5.
Final Answer:
There are 16 rows.
The number of logs in the top row is 5.
Question 20
In a potato race, a bucket is placed at the starting point, which is 5 m from the first potato and other potatoes are placed 3 m apart in a straight line. There are ten potatoes in the line.
A competitor starts from the bucket, picks up the nearest potato, runs back with it, drops it in the bucket, runs back to pick up the next potato, runs to the bucket to drop it in, and she continues in the same way until all the potatoes are in the bucket. What is the total distance the competitor has to run?

[Hint: to pick up the first potato and the second potato, the total distance (in metres) run by a competitor is 2 × 5 + 2 ×(5 + 3)]
Answer:
The distances of the potatoes from the bucket are 5, 8, 11, 14 meters, and so on. The competitor runs two times the distance for each potato, as she has to go to the potato and then return.
Thus, the distances to be run are: 10, 16, 22, 28, 34, and so on.
Given:
a = 10 (the distance for the first potato),
d = 6 (common difference between each distance).
We need to find the total distance run by the competitor for 10 potatoes. We use the formula for the sum of an arithmetic series: S_n = n/2 × [2a + (n – 1) × d]
Substituting the values: S_10 = 10/2 × [2(10) + (10 – 1) × 6] S_10 = 5 × [20 + 54] S_10 = 5 × 74 S_10 = 370 meters.
Therefore, the total distance the competitor will run is 370 meters.
__________________